Understand the complexities of substance use disorder and discover effective treatment options in this comprehensive article.

Our dedicated team of professionals is committed to providing comprehensive, evidence-based treatment. This helps address the underlying causes of SUD and empowers clients to reclaim their lives.
"Adapting treatment plans for substance use disorders in response to changing societal norms and legal statuses involves staying informed and flexible. As societal attitudes and laws evolve, we update our understanding and approach to substances like cannabis. This includes educating patients about the potential risks and benefits, considering their unique circumstances, and addressing any misconceptions they might have. We also tailor our treatment strategies to reflect the current legal context, ensuring our methods are relevant and effective. By staying adaptable, we can provide the best possible care in a shifting landscape."
New Choices Treatment Centers Medical Services Team Tweet
"Family dynamics are crucial in the treatment and management of substance use disorders. A supportive family can enhance recovery by providing emotional support and accountability. Conversely, dysfunctional dynamics, such as enabling behaviors or conflicts, can hinder progress. Family therapy helps address these issues, educates family members about addiction, and fosters a supportive environment, aiding in the overall recovery process."
New Choices Treatment Centers Medical Services Team Tweet

"Addressing both the psychological and physiological aspects of substance use disorders is crucial for comprehensive and effective treatment. Physiologically, substance use affects the brain and body, leading to dependence and withdrawal symptoms. Proper medical care is necessary to manage detoxification and stabilize the individual physically. Psychologically, substance use disorders often involve underlying emotional and mental health issues, such as depression, anxiety, or trauma. These issues can drive the cycle of addiction, making it essential to address them through therapy and counseling. By treating both the physical and mental aspects, we can provide holistic care that supports overall recovery."
New Choices Treatment Centers Medical Services Team Tweet
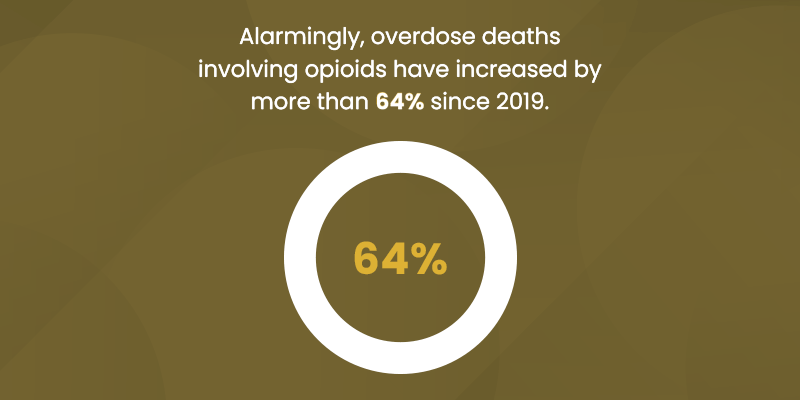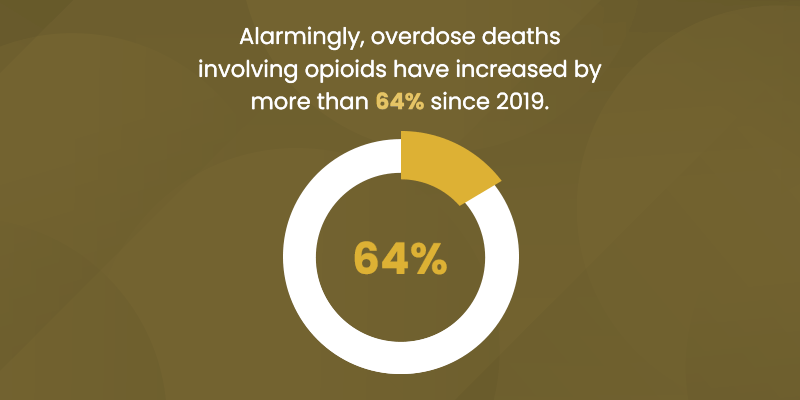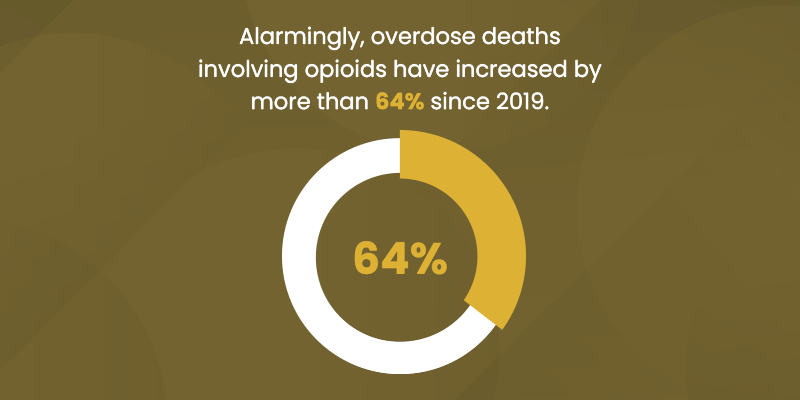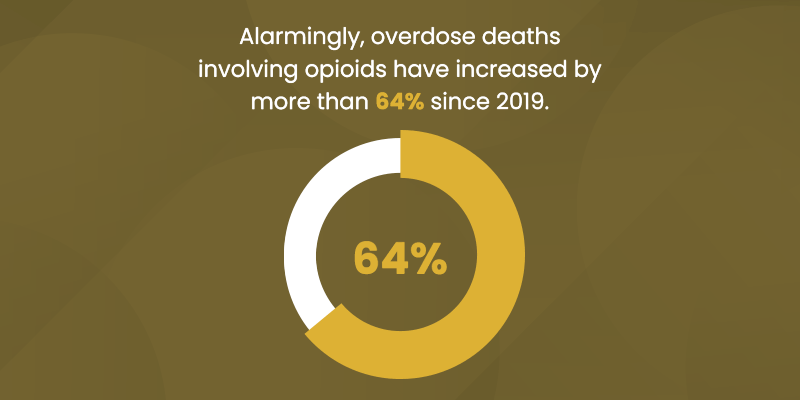
"According to the latest guidelines in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), a substance use disorder is diagnosed based on specific criteria. The DSM-5 outlines 11 criteria that can help determine the severity of the disorder, which is categorized as mild, moderate, or severe depending on how many criteria are met: 1. Taking the substance in larger amounts or for longer than intended. 2. Wanting to cut down or stop using the substance but not being able to. 3. Spending a lot of time getting, using, or recovering from use of the substance. 4. Cravings and urges to use the substance. 5. Not managing to do what you should at work, home, or school because of substance use. 6. Continuing to use, even when it causes problems in relationships. 7. Giving up important social, occupational, or recreational activities because of substance use. 8. Using substances again and again, even when it puts you in danger. 9. Continuing to use, even when you know you have a physical or psychological problem that could have been caused or made worse by the substance. 10. Needing more of the substance to get the effect you want (tolerance). 11. Development of withdrawal symptoms, which can be relieved by taking more of the substance. To diagnose an SUD, a professional will look at the individual's behavior over the past 12 months. Meeting 2-3 of these criteria typically indicates a mild disorder, 4-5 suggest a moderate disorder, and 6 or more indicate a severe substance use disorder."
New Choices Treatment Centers Medical Services Team Tweet
Treating substance use disorder(s) and any co-occurring mental health challenges involves multiple strategies tailored to individual needs. These approaches help address both the physical and psychological aspects of addiction.
"Treating patients with multiple substance use disorders can be particularly challenging due to the complex nature of their condition. The interactions between different substances can complicate detox and treatment processes. Additionally, patients often face co-occurring mental health issues that need to be addressed simultaneously. Developing a personalized treatment plan that addresses all aspects of their substance use and mental health is crucial for effective recovery. Despite these challenges, comprehensive and tailored care can lead to successful outcomes."
New Choices Treatment Centers Medical Services Team Tweet
"Incorporating evidence-based practices involves using scientifically validated approaches throughout the treatment process. This starts with a thorough assessment to develop a personalized treatment plan. We utilize therapies like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT) to address the underlying behaviors and thoughts associated with substance use. When appropriate, medications are prescribed to help with detox, reduce cravings, and manage withdrawal symptoms. For patients with co-occurring mental health issues, integrated care is provided to treat both conditions simultaneously. Continuous monitoring ensures the treatment plan remains effective and is adjusted as needed to support the patient’s recovery journey."
New Choices Treatment Centers Medical Services Team Tweet

